- What is Shingles ?
- Who can be effected from Shingles ?
- What are the symptoms and complications of Shingles ?
- Prevention and Vaccine
- Treatment procedures
What is Shingles ?
Shingles ( also known as herpes zoster ) is a viral infection that can usually occur in adults and cause painful rashes .
People exposed to chickenpox in the past may be at a higher risk of getting shingles . The cause of reactivation of the virus is still unknown . Herpes zoster infection can occur in any part of the patients body .
Who can be effected from shingles ?
Anyone who has been effected by chickenpox is vulnerable to shingles . There are many factors that weaken your immunity against shingles and make a person more prone to get the infection . These include –
Age : occurs mostly in people above the age of 50 . People above 60 might experience more complicated symptoms .
Previous medical history and treatments : From diseases like diabetes to much severe infections like HIV/AIDS and cancer , any disease that hampers your immunity might increase your risk of shingles . Radiation / chemotherapy and other such long term treatments can also lower your bodies ability to fight with infections and may trigger shingles . Long term use of steroids , medicines used after organ transplants can also elevate your risk of getting shingles .
What are the symptoms and complications of Shingles ?
herpes zoster infection generally causes a painful rash that may appear as a stripe of blisters on the dermatomal distribution of the skin .
The patient might experience pain even when the rash is gone ( post herpetic neuralgia )
The pain and feeling during the infection may be described in easy language as a feeling of pricking ones skin with multiple needles and pins at multiple rash spots during the same time .
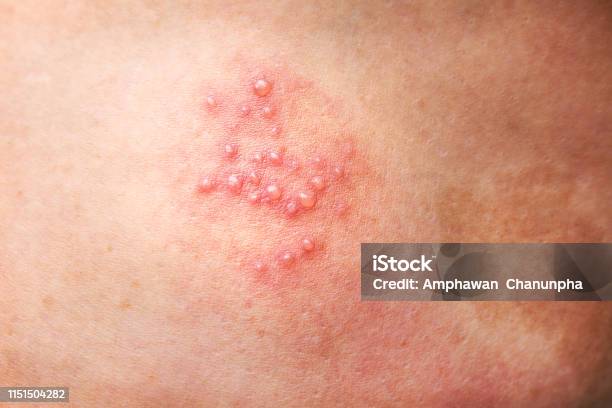
Complications from shingles include
Post herpetic neuralgia – pain that occurs even after the rash and blisters of shingles have gone . This occurs due to damaged nerve fibres sending confused messages from the skin to brain .
Loss of vision : shingles in or around the eye may cause infections with extreme pain and also lead to loss of vision .
Neurological issues : it might lead to encephalitis , paralysis of face , or problems with ear nose and throat.
skin infections might also occur if shingles blisters are not properly treated .
Prevention and Vaccine
A shingles vaccine is the most sought of way to prevent shingles . However , it doesn’t guarantee to protect you from shingles completely , but this likely reduces the course complications and severity of the disease . Shingles vaccine may also lower the risk of postherpetic neuralgia .
SHINGRIX VACCINE :
Shingrix is indicated for prevention of shingles and postherpetic neuralgia in adults above 50 years of age . The primary vaccination schedule consists of 2 doses of 0.5 ml each , at a gap of 2 months .
ZOSTAVAX VACCINE :
Zostavax is indicated in adults above 50 years of age . It contains weakened varicella zoster virus . It works by helping immune system to protect you from getting shingles . It is administered as single dose of 0.65 ml subcutaneously in the deltoid region of the upper arm .
Treatment procedures
If you experience any symptoms of shingles , you should consult a good general physician or dermatologist as soon as possible and avoid public contact of affected area .
Treatment generally includes antivirals ( acyclovir , valacyclovir , famciclovir ) and NSAIDs ( aceclofenac, diclofenac , acetaminophen) which may be topical or oral and numbing creams such as lignocaine or prilocaine .
*Any sort of treatment shall strictly be done under medical supervision . Above information is just to impart knowledge and not a medical advice . *
sources : unsplash.com , HTTPS://mayoclinic.org , google.com , shingrix.com ,1mg.com
CONTACT US : THEPHARMACISTGUY.COMContact us
